Targeted Therapy in Cancer: Precision Medicine for Promising Outcomes
Introduction: Targeted therapy has revolutionized the field of cancer treatment, offering hope and promising outcomes for patients diagnosed with various types of cancer. Unlike traditional chemotherapy that attacks both cancerous and healthy cells, targeted therapy focuses on specific molecular alterations or pathways that fuel cancer growth. This approach allows for more precise and personalized treatment, minimizing side effects and increasing the chances of successful outcomes. In this article, we delve into the concept of targeted therapy in cancer and explore its potential impact on improving patient outcomes.
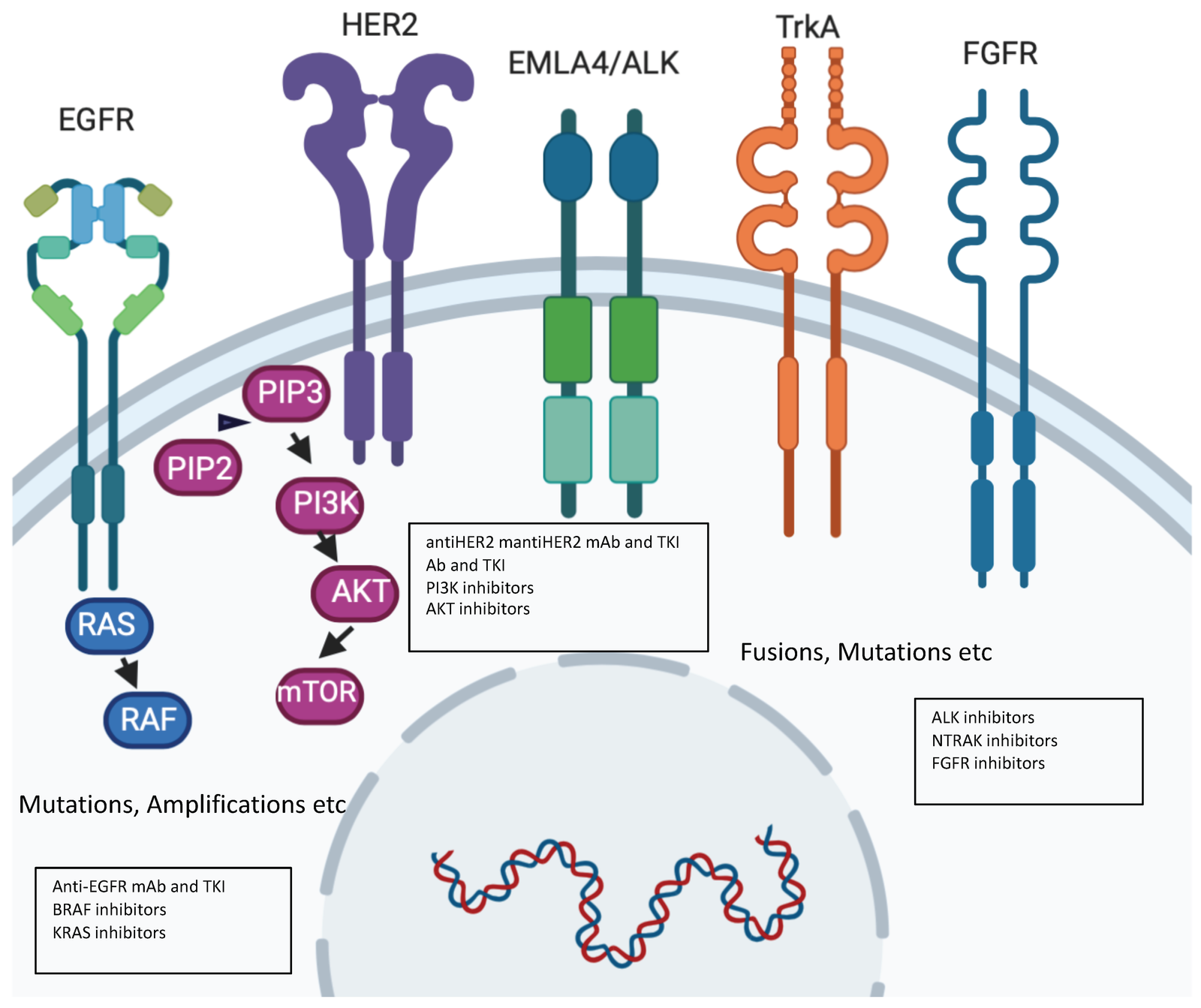
Understanding Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets specific molecules or genetic mutations that drive cancer growth. These alterations can be found on the cancer cell surface, within the cell, or even in surrounding tissues that support cancer growth. These alteration in cancer cells can be found out by using sophisticated molecular tests like Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) or RT-PCR on the tumour tissue or blood sample. By pinpointing these specific targets, oncologists can tailor treatment to address the unique characteristics of each patient’s cancer, maximizing the therapeutic benefit.
Immunotherapy in Cancer: Empowering the Body's Defenses to Fight Back
Introduction:
Immunotherapy has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in cancer treatment, harnessing the power of the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Unlike traditional cancer therapies, which directly target cancer cells, immunotherapy enhances the body’s natural defences to combat cancer more effectively. In this article, we delve into the concept of immunotherapy in cancer and explore its transformative potential in revolutionizing the landscape of cancer care.
Understanding Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a form of cancer treatment that stimulates or strengthens the immune system’s ability to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. The immune system’s primary function is to defend the body against harmful invaders, including viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells like cancer. However, cancer cells can evade the immune system’s detection by using various mechanisms to disguise themselves as normal cells. Immunotherapy seeks to overcome these evasion tactics and enhance the immune response against cancer.
Dr. Suresh Kumar B: Your Expert in Immunotherapy for Cancer
When it comes to cancer treatment, having an experienced and skilled oncologist is paramount to ensure the best possible outcomes. Dr. Suresh Kumar B, is a renowned expert in the field of immunotherapy for cancer, whose dedication and expertise have transformed the lives of countless patients.
Dr. Suresh Kumar brings with him a wealth of knowledge and experience of immunotherapy, having treated hundreds of patients with immunotherapy at Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. With a distinguished background in oncology and a passion for cutting-edge research, he is at the forefront of innovative treatments that harness the power of the immune system to fight cancer.
Immunotherapy in Cancer: Empowering the Body's Defenses to Fight Back
Introduction:
Chemotherapy has been a cornerstone in cancer treatment for many years, providing hope and improved outcomes for millions of patients worldwide. As one of the most widely used cancer therapies, chemotherapy involves the administration of powerful drugs to target and destroy cancer cells. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the concept of chemotherapy for cancer, its mechanisms of action, and its role in the fight against this formidable disease.
Understanding Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment, meaning it circulates throughout the body to reach cancer cells wherever they may be located. Unlike surgery or radiation therapy, which target specific tumor sites, chemotherapy can treat both localized and metastatic cancers, making it a versatile option for various cancer types.

State-of-the-Art Cancer Treatment
Staying up-to-date is crucial for an oncologist to provide the best possible care for cancer patients. Cancer research and treatment are constantly evolving fields, with new discoveries, technologies, and treatment modalities emerging regularly. Here are some reasons why an oncologist needs to be up to date:
Advances in Treatment: New treatment approaches, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapies, have revolutionized cancer care, offering more effective and less toxic options. An up-to-date oncologist can offer these cutting-edge treatments, potentially leading to better outcomes for their patients.
Precision Medicine: With advancements in genomic testing, oncologists can identify specific genetic mutations in a patient’s cancer, allowing for personalized and targeted treatment plans. Staying current with these technologies enables oncologists to provide more tailored and precise therapies.
Clinical Trials: Ongoing clinical trials are essential for testing and validating new treatment strategies. Being up-to-date allows oncologists to identify relevant clinical trials for their patients, providing access to potentially life-saving therapies not yet widely available.
Side Effect Management: Knowledge of the latest supportive care strategies helps oncologists minimize the side effects of cancer treatments, improving the overall quality of life for their patients during and after therapy.
HORMONAL THERAPY
Hormonal Therapy for Cancer: A Powerful Weapon against Hormone-Responsive Tumors
Introduction: Hormonal therapy, also known as endocrine therapy, has emerged as a powerful and targeted approach in the treatment of hormone-responsive cancers. This specialized treatment option is designed to interfere with the hormones that fuel the growth and spread of certain types of cancer
Understanding Hormone-Responsive Cancers: Hormone-responsive cancers, such as breast, prostate, and uterine cancers, have specific receptors on their cells that interact with hormones, such as estrogen or testosterone. These interactions stimulate cancer cell growth and proliferation. Hormonal therapy is particularly effective in these cases, as it targets these hormone receptors, inhibiting their activity and thwarting cancer growth.